Login to your account
- Prescription included
- Genuine medication
- All-inclusive service - No hidden fees
- Free next-day delivery
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Buy STI treatments with an online prescription
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are spread through close physical contact and are very easy to catch. Globally, more than 1 million cases of STIs are acquired every day.
As many as a quarter of these infections are symptomless, making them even easier to spread.
There are many different kinds of sexual infections. They can be caused by bacteria, viruses or even parasites. Some STIs can be cured with a course of medication, while others can be managed long-term with the correct treatment.
Keep reading to learn more about STIs, including means of prevention, available treatment options and sexual screening.
Available Conditions
Genital Warts
Genital warts are one of the most common forms of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in Europe. They are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) and are very infectious. They are small itchy bum...
Symptoms
Women
- Small, fleshy growths (warts) on:
- The vulva or inside the vagina
- On the cervix
- Around or inside the anus
- On the upper thighs
Men
- Small, fleshy growths (warts) on:
- The penis or scrotum
- Inside the urethra
- Around or inside the anus
- On the upper thighs
Our Service
- In Stock, dispatched today
- Free delivery next working day
- Online prescription - No doctor appointment
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in the UK and can be treated and cured fully with a course of antibiotics. Usually diagnosed in younger men and women between the ages of 16 and 25, chlamydia and its sympt...
Symptoms
Women
- Cystitis
- Change in vaginal discharge
- Mild lower abdominal pain
Men
- Discharge from the penis
- Irritation at the tip of the penis (urethra)
Our Service
- In Stock, dispatched today
- Free delivery next working day
- Online prescription - No doctor appointment
Genital Herpes
Genital herpes is a highly contagious and common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus. The virus causes itchy red genital sores and fluid blisters on the skin. Unfortunately, the virus is not curable and can lay...
Symptoms
Women
- (Primary Infection)
- Small blisters or ulcers on the genitals, rectum, anus, thighs and cervix
- Tingling, itching or burning sensation around the sores
- Pain when urinating
- Clear, white or pale yellow vagina discharge
- Cold/flu symptoms e.g. muscle aches, fever and nausea
Men
- (Primary Infection)
- Small blisters or ulcers on the genitals, rectum, anus and thighs
- Tingling, itching or burning sensation around the sores
- Pain when urinating
- Cold/flu symptoms e.g. muscle aches, fever and nausea
Our Service
- In Stock, dispatched today
- Free delivery next working day
- Online prescription - No doctor appointment
Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis (BV), also known as gardnerella vaginosis, is an extremely common bacterial vaginal infection that affects women. BV can be a discomforting condition caused by a combination of naturally occurring vaginal bacteria. Bacterial va...
Symptoms
Women
- Discharge that is:
- White or grey in colour
- Thin or watery
- Has an unusual smell (strong fishy odor)
Men
- n/a
Our Service
- In Stock, dispatched today
- Free delivery next working day
- Online prescription - No doctor appointment
Non-Specific Urethritis
Non-specific urethritis (NSU) is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) in men, though women can also get it. It is mainly caused by other STIs such as chlamydia or gonnorhoea.
It caus...
Non-specific urethritis (NSU) can affect both men and women and is classified as a bacterial STI. It is most often spread by other STIs, particularly chlamydia. Urethritis occurs when the urethra becomes inflamed, and the term "non-specific" refers to the fact that the direct cause of this particular infection is not yet understood. NSU is easily treated with a course of antibiotics.
Our Service
- In Stock, dispatched today
- Free delivery next working day
- Online prescription - No doctor appointment
Mycoplasma Genitalium
Mycoplasma genitalium (MGen) is a common infection which is straightforward to treat. However, it doesn’t always present with symptoms, meaning it can be difficult to detect.
The best way of treating MGen is with a specific course of anti...
Mycoplasma genitalium is a bacterial sexually transmitted infection, which can be difficult to diagnose. It is usually asymptomatic and can occur in both men and women. If Mycoplasma genitalium is left untreated, it can lead to prostatitis in men and urethritis in women, and even infertility in both sexes. However, it can easily be treated with antibiotics.
Our Service
- In Stock, dispatched today
- Free delivery next working day
- Online prescription - No doctor appointment
Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) that is caused by the Trichomonas vaginalis (TV) parasite.
It is known to affect both men and women and is passed on during unp...
Trichomonas vaginalis is a sexually transmitted infection that is caused by an organism called a protozoan - or parasite - which is transferred during unprotected sex. This protozoan primarily affects the urethra and is more commonly found in women, though the infection does occur in men. The parasite is similar in size to a white blood cell and is mobile through the vaginal and urethral tissues, which causes tissue ulceration.
Our Service
- In Stock, dispatched today
- Free delivery next working day
- Online prescription - No doctor appointment
Ureaplasma Urealyticum
Ureaplasma Urealyticum (UU) is a very common bacterial infection that affects both men and women.
Whilst it is easily transmittable during sexual contact, it isn’t always classed as an STI (s...
Ureaplasma urealyticum is one of the most common bacterial STIs, affecting almost 70% of both women and men. It can be transmitted through unprotected sexual contact, as well as through blood and saliva. It is highly contagious and often does not display any symptoms. If it is not treated with antibiotics, it can lead to infertility.
Our Service
- In Stock, dispatched today
- Free delivery next working day
- Online prescription - No doctor appointment
What are STIs?
STIs are infections that are passed on through close, intimate contact - usually sex. They are very common and easy to catch as many cases do not present with symptoms.
While STIs aren’t life-threatening, they can have serious consequences if not treated promptly. If you have sex with multiple partners, you must get checked regularly for STIs to keep yourself and others safe from these potential risks.
Full list of STIs
This list covers some of the most common sexually transmitted infections, including bacterial, viral, parasitic and common conditions that are often mistaken for STIs.
| Bacterial | Viral |
|---|---|
|
|
| Parasitic | Often mistaken for STIs |
|---|---|
|
|
What are the symptoms of STIs?
The symptoms of STIs vary depending on what infection you have. However, many common bacterial infections have no symptoms at all.
This highlights the importance of getting tested regularly and using barrier methods of contraception (such as condoms) when engaging in sex with new partners.
Common STI symptoms
The following symptoms are common indications that you’ve caught an STI:
- a painful or burning sensation when urinating
- itching, burning or tingling around the genitals
- blisters, warts or sores around the genitals
- unusual bleeding or discharge
- unusual pain during sex
Bacterial STI symptoms
Symptoms vary between different kinds of sexual infections. Bacterial infections may cause:
- bleeding after sex or between periods
- pelvic or lower abdominal pain
- pain during sex or urination
- unusual discharge from the penis, vagina or anus
- irritation, soreness or itching around your genital area
Bacterial STIs can be cured with antibiotic treatments such as Azithromycin or Doxycycline.
Viral STI symptoms
If you’ve contracted a viral STI, you will get symptoms eventually. However, they often don’t show up for weeks, months or even years.
Viral STI symptoms cannot be cured, but they can be managed with the right treatment. For most people, symptoms lie dormant for most of the time, with flare-ups occurring every few months or so.
Genital herpes symptoms include:
- tingling sensation around the genital area
- dark patches on skin
- sores around the penis, vagina, anus or groin area
- swollen glands
- abdominal pains
We offer 3 treatments for genital herpes: Valtrex, Famvir and Aciclovir.
Genital warts symptoms include:
- single or groups of small growths on and around the genitals
- disruption to your urine flow (if internal growths are present)
We offer 3 treatments for genital warts: Aldara, Condyline and Warticon.
Symptoms in men vs women
Generally, men are less likely to experience STI symptoms compared to women. However, it is still important to be aware of potential symptoms and the conditions they’re linked with.
| Male symptoms | Female symptoms | |
|---|---|---|
Chlamydia: |
|
|
Gonorrhoea: |
|
|
Hepatitis: |
|
|
Genital warts (HPV): |
|
|
Genital herpes: |
|
|
Trichomoniasis: |
|
|
If you experience any of the symptoms found in this table, visit a sexual health clinic and get tested at your earliest convenience. Avoid having any unprotected sex if you think you may have contracted an STI.
What are the causes of STIs?
STIs are often highly contagious and can be found in semen, vaginal secretions, blood and occasionally saliva. In most cases, people catch STIs through penetrative vaginal or anal sex.
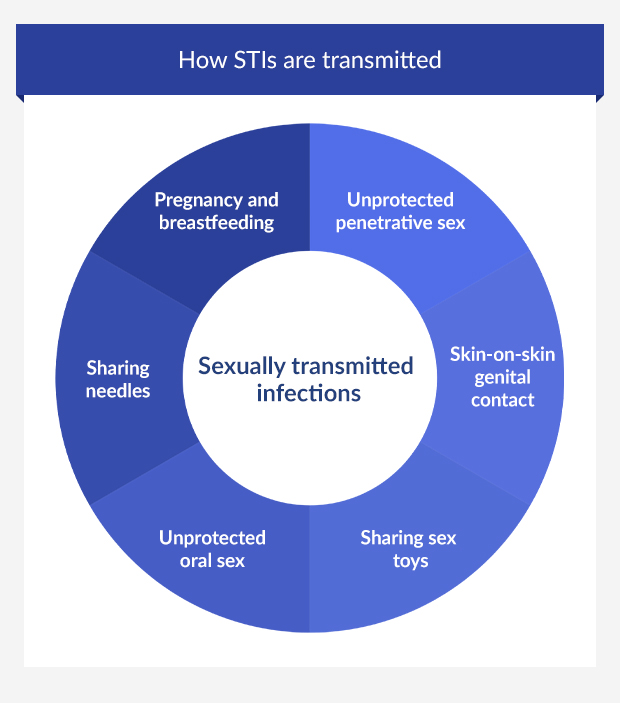
An infection can be spread as soon as sexual contact is made. You can catch an STI even if the man doesn’t ejaculate, or if the penis doesn’t fully enter the vagina. Skin-to-skin contact is enough.
STIs can also be passed on via unprotected oral sex and the sharing of sex toys. To practise safe sex, ensure that both parties are wearing either a condom or a dental dam, and wash sex toys in between uses.
Can you get an STI without having sex?
It is possible to catch some sexually transmitted infections without having sex.
STIs can be spread through blood (such as the sharing of needles), and pregnant women can also pass on an infection to their unborn child.
Can you get an STI by kissing?
Oral herpes (HSV-1) can be passed on through kissing, although cold sores are not considered to be a sexually transmitted infection.
In rare cases, someone who catches genital herpes (HSV-2) via oral sex may be able to pass the infection onto someone else by kissing. Both strains of the herpes virus can occur on both the face and genitals.
What can happen if an STI goes untreated?
STIS can cause severe, life-long conditions if left untreated. This is the case even when an infection is asymptomatic.
Complications of an untreated STI include:
- infertility
- mother-to-child transmission
- chronic pain
- sexual dysfunction
- pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- increased chance of developing HIV
- bladder problems
Getting tested
As so many STI cases are asymptomatic, you must get regular sexual health screening if you are engaging in unprotected sex with multiple partners. This prevents you from developing any serious conditions and protects others from catching possible infections.
Most sexually transmitted infections can be detected through urine or blood samples. Some specific conditions may require a swab from the inside of your mouth or your genitals.
To get screened for potential STIs, make an appointment with your local surgery or sexual health practice. Some practices offer drop-ins, so you don’t have to book in advance.
How can I treat an STI?
Bacterial STIs are usually treated with a round of antibiotics that help your body fight off the infection. These types of infections are entirely curable - but they can return if you don’t take your treatment as prescribed.
Viral STIs like genital herpes and HIV cannot be cured. But you can take medication that makes these conditions more manageable.
Can I buy STI treatment online?
Yes, you can purchase treatments for many kinds of STIs online here at euroClinix. We currently provide medications for:
- genital warts
- chlamydia
- bacterial vaginosis (BV)
- non-specific urethritis
- mycoplasma genitalium
- trichomonas vaginalis
- ureaplasma urealyticum
It is important to get a diagnosis for your STI before starting a certain treatment. Many STIs have similar symptoms and can be mistaken for one another. The easiest way to get a diagnosis is to get tested at a local sexual health practice.
Further reading

The Effects of Alcohol on Antibiotics: Complete Safety Guide
Reviewed by Dr. Caroline Fontana
Chlamydia in the Mouth: Symptoms, Causes & Effective Trea...
Reviewed by Dr. Caroline Fontana
5 foods to eat while on antibiotics
Reviewed by Dr. Caroline Fontana
Burning sensations after sex: causes, treatments and when...
Reviewed by Dr. Caroline Fontana
Metronidazole side effects & how to manage them
Reviewed by Dr. Caroline Fontana

What genital warts look like and what causes them
Reviewed by Dr. Caroline FontanaSelect
medicationFill out a short
medical formDoctor issues
prescriptionMedication sent
from pharmacy
