Login to your account
- Prescription included
- Genuine medication
- All-inclusive service - No hidden fees
- Free next-day delivery
The combined oral contraceptive pill
Get combined hormonal contraception with an online prescription
The combined pill is one of the most popular forms of contraception due to its simplicity and effectiveness. You take it once daily and you’re fully protected against pregnancy.
At euroClinix, we offer a wide range of different hormonal contraceptive options. Simply pick the brand you use, complete a consultation and receive it shortly afterwards.
On this page
What is the combined oral contraceptive pill? How does the pill work? What types of combined oral contraceptive pills are available? What are the benefits of taking birth control pills? How do I take it? What do I do if I miss a pill? What are the side effects of ‘the pill’? What are the risks of taking ‘the pill’? What are the side effects of coming off the pill? Can I buy the pill online?Available Conditions

- Single daily dose
- 99% effective at preventing pregnancy
- Can improve PMS symptoms
- Contains a 'third generation' version of progestogen, making it safer for most women
- Over 99% effective at stopping pregnancy
- Proven to make periods lighter, less painful and more regular

- Prevents pregnancy
- Mimics the natural menstrual cycle
- Convenient dosing

- Over 99% effective
- Reliable daily contraception
- Eases period discomfort

- Effective hormonal contraceptive pill
- Over 99% effective when used correctly
- Lower dose of oestrogen
- Relieves period cramps
- Once daily dose
- Over 99% effective when taken correctly
- 99% effective at preventing pregnancy
- Reduces symptoms associated with PMS
- Easy to take over for 21 days followed by a seven-day break

- Regulates menstrual cycle
- 99% effective at preventing pregnancy
- Can treat heavy menstrual bleeding
- Provides protection from pregnancy in a convenient daily tablet
- Proven treatment for endometriosis and premenstrual symptoms
- Taken for 21 consecutive days, followed by a seven day break
- 99% effective at preventing pregnancy
- Can alleviate menstrual symptoms
- Available in three-month and six-month supplies
What is the combined oral contraceptive pill?
The combined oral contraceptive pill (COCP) is a form of hormonal contraception containing a combination of two hormones. The COCP is most commonly known as just ‘the pill’.
Unlike the progesterone-only pill (POP or ‘mini-pill’), which only contains one hormone, the COCP contains 2 synthetic female hormones, oestrogen and progesterone. These mimic the hormones made naturally in the ovaries and work in different ways to protect against pregnancy.
How effective is ‘the pill’?
When taken correctly, it is over 99% effective at preventing pregnancy. Some hormonal combinations may be more effective than others for treating certain conditions such as acne.
How does the pill work?
The COCP works in different ways to prevent pregnancy. Once a month, your ovaries release a mature egg that travels down the fallopian tubes towards the uterus (womb). This is a process called ovulation.
While ovulation happens, the lining of your womb begins to thicken as it prepares to host a fertilised egg. At the same time, the mucus in the cervix becomes thinner to make it easier for sperm to reach the womb.
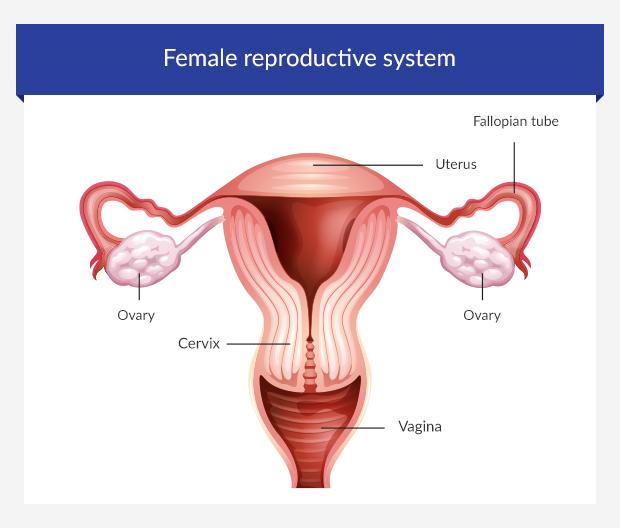
The combined pill stops all of the following processes.
- It stops the ovaries from releasing an egg each month.
- It thickens the cervical mucus, making it harder for sperm to enter the womb and reach an egg.
- It thins the lining of the womb, which makes it difficult for a fertilised egg to implant into the womb and grow.
What types of combined oral contraceptive pills are available?
With a wide variety of contraceptive pills available, your doctor can advise you on the correct pill for you.
The main types of combined pills available are monophasic and multiphasic. They differ in how many doses of hormones there are across the pack and how many pills the packs contain.
Monophasic pills
These are the most common type of combined pill and are usually what doctors prescribe for first-time users.
Each tablet contains the same amount of hormones across the pack. One tablet is taken each day for 21 days, followed by a break for the next 7 days where you will get a withdrawal bleed. When you finish your 7-day break, you should start your next pack, even if you are still bleeding.
The most common monophasic brands include:
Some packs of monophasic pills contain 28 tablets in total. Of these, 21 are active tablets and 7 are inactive tablets (or a variation of this combination). This means that one tablet is taken daily for 28 days with no break in between packs.
This might be a good option if you prefer to take a tablet every day without a break so you don’t forget when to stop and start. During the days you take the inactive tablets, you will get a ‘withdrawal bleed’.
Examples of these pills include Microgynon 30 ED, Femodene ED, Eloine and Zoely.
Multiphasic pills
Multiphasic pills contain various sections within a pack and each section contains different amounts of hormones. Each section is marked by different coloured tablets. The varying amounts of hormones are thought to copy the way your hormones fluctuate during your menstrual cycle. You must take these tablets in the correct order for them to be effective.
Multiphasic pills are available in packs of 21 and 28 tablets. The 21-day pills are taken once a day followed by a 7-day break. The 28-day pills are taken every day however, the last 7 tablets in the pack do not contain any hormones.
The 3 types of multiphasic pills are:
- Biphasic (e.g. Binovum) where the level of progestogen changes about halfway through the cycle. The level of oestrogen stays the same throughout.
- Triphasic (e.g. Logynon) where there is a change in the dose of hormones 3 times during the cycle.
- Quadriphasic (e.g. Qlaira) where there is a change in the dose of hormones 4 times during the cycle.
What are the benefits of taking birth control pills?
The main benefit of contraceptive pills is that they prevent pregnancy. However, there are several additional benefits, such as:
- making your periods more regular or they can be used to skip your periods
- reducing menstrual cramps
- reducing PMS symptoms such as mood swings and irritability
- making your periods lighter
- improving your skin and reducing outbreaks of acne
- helping with symptoms of endometriosis and PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome)
- reducing the risk of womb and ovarian cancers
Consult with your doctor if you’re looking to improve a specific symptom or condition.
The pill will not prevent you from contracting sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Use a condom for STI protection and visit a sexual health clinic if you’re concerned you have an STI.
How do I take it?
The most important part of taking oral contraceptives is that you take them at the same time each day. Taking a tablet too late or missing one could reduce its effectiveness.

How you take it will depend on what type of pill it is. Your doctor will explain how to take this medication. You can also refer to your patient information leaflet for more information.
When to start the pill
For immediate protection against pregnancy, start taking the active tablets within the first 5 days of your period.
You can start 'the pill' at any other time during your cycle, however, you will need to use a barrier method of contraception for the next 7 days before you are protected.
How do I delay my period on the pill?
You can also use the combined pill to delay your periods. If you take a 21-day pill, simply skip the 7-day break and immediately start your next pack. Similarly, if you take an everyday pill, you can skip the inactive tablets and immediately start the next strip of active tablets.
You can only skip your period with combined hormonal pills. If you take a progestin-only pill (POP or mini pill), take every pill in your pack.
When can I take the pill after giving birth?
When deciding what contraception to use after birth, how soon you can take it plays a big part in the decision.
If you’re not breastfeeding, you can take the combined pill 3 weeks after giving birth however, you will need to check with your doctor. If you are breastfeeding, you must wait at least 6 weeks after giving birth to take this medicine. If in doubt, consult your midwife or doctor.
If you have just had an abortion or miscarriage, you can start taking it immediately. If you take it within 5 days of an abortion or miscarriage, it will be effective straight away. Otherwise, you will need to use additional forms of birth control (like condoms) until you have taken an active tablet for 7 days in a row.
What do I do if I miss a pill?
If you are more than 24 hours late (or 12 hours for certain COCPs), or if you frequently miss tablets, this medicine will be less effective at preventing pregnancy. It's important to use additional contraception if you have missed two or more tablets in your blister pack. You may need to seek emergency contraception if you have had sex during this time.
Advice for missing a pill is different for each type of pill, and in which week in your pack this occurred, so ensure you read the patient information leaflet thoroughly.
Use our interactive tool below on what to do if you miss one or multiple tablets in one month (menstrual cycle). Simply click to begin.
Use our interactive tool below on what to do if you miss one or multiple pills in one month (menstrual cycle). Simply click to begin.
You may be at risk of pregnancy. Please see your own doctor for advice and follow-up.
You are still fully protected, as long as you:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the pack as normal.
You are still fully protected, as long as you:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the pack as normal.
You are still fully protected, as long as you:
1) Take the missed pill and take the active (21) pills as per the normal schedule.
2) Skip the pill-free break.
3) Start the new pill pack straight away.
If your pill pack contains 21 tablets, your 4th week should be a pill-free week if you have not chosen to skip it. This means you should still be fully protected, as long as you:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal.
You may be at risk of pregnancy. Please see your own doctor for advice and follow-up.
The combined pill may not be as effective. You should follow the below advice:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal. You may need to take two pills in one day.
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex for the following 7 days.
If you vomited within 3-4 hours of taking the pill, you should take a new pill no longer than 24 hours before your usual pill time. As long as you are not sick again, you should still be protected against pregnancy. If you are sick again or you do not take a new pill, your contraception will not be effective. If that is the case, retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
You should still be protected against pregnancy. Take your next pill as per your usual schedule.
You should still be protected against pregnancy. Take your next pill as per your usual schedule.
If you have had severe diarrhoea for more than 24 hours, the pill may not have been fully absorbed and therefore may not be as effective. You should treat every 24 hours of severe diarrhoea as a missed pill. Retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
You may be at risk of pregnancy. Please see your own doctor for advice and follow-up.
You are still fully protected, as long as you:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the pack as normal.
You are still fully protected, as long as you:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the pack as normal.
You are still fully protected, as long as you:
1) Take the missed pill and take the active (21) pills as per normal schedule.
2) Skip the inactive (placebo) pills / the pill-free break.
3) Start the new pill pack straight away.
If you missed an inactive pill (placebo), in the 4th week of your cycle, you will still be protected from pregnancy.
You may be at risk of pregnancy. Please see your own doctor for advice and follow-up.
The combined pill may not be as effective. You should follow the below advice:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal. You may need to take two pills in one day.
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex for the following 7 days.
If you vomited within 3-4 hours of taking the pill, you should take a new pill no longer than 24 hours before your usual pill time. As long as you are not sick again, you should still be protected against pregnancy. If you are sick again or you do not take a new pill, your contraception will not be effective. If that is the case, retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
You should still be protected against pregnancy. Take your next pill as per your usual schedule.
You should still be protected against pregnancy. Take your next pill as per your usual schedule.
If you have had severe diarrhoea for more than 24 hours, the pill may not have been fully absorbed and therefore may not be as effective. You should treat every 24 hours of severe diarrhoea as a missed pill. Retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
The combined pill may not be as effective. If intercourse took place in the week prior, the possibility of a pregnancy should be considered. Contact a doctor for advice and consider using an emergency contraceptive method.
You should keep these key points about taking this pill in mind:
1) The more 'white active tablets' are missed and the closer the missed tablets are to the 4 yellow placebo tablets, the higher the risk of pregnancy.
2) 7 days of uninterrupted 'active tablet'-taking are required to attain adequate protection against pregnancy. If you have trouble remembering to take your pill consistently, you should speak to your doctor for advice.
You are still fully protected, as long as you:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the pack as normal.
Provided you have only missed one pill and taken the pills correctly the week prior, you should still be protected against pregnancy.
You should:
1) Take the missed pill or start a new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal. You may need to take two pills in one day.
If you have missed more than 1 tablet or have not taken the pills consistently the week pior, you should use a barrier contraceptive method for the following 7 days.
If you have missed a pill in the last week of active tablets, the risk of pregnancy is higher. You should still be protected if you have taken the active pills uninterrupted the 7 days before and you take the following advice:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal. You may need to take two pills in one day.
If you have missed more than 1 tablet or have not taken the pills consistently the week prior, you should use a barrier contraceptive method for the following 7 days.
If you missed one of the last 4 pills of the pill pack, it should have no impact as these are hormone-free pills. You should:
1) Dispose of the missed pill and take the next scheduled pill at the correct time, ensuring you don't go longer than 4 days before you start a new pack with active pills.
2) You can also start a new pill pack straight away. This changes the first day of your cycle.
If you had sex the week before missing your pill, you may be at risk of pregnancy. Contact your doctor for advice and consider using an emergency contraceptive method. You should also follow the below advice:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal. You may need to take two pills in one day.
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 7 days.
The combined pill may not be as effective. You should follow the below advice:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal. You may need to take two pills in one day.
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 7 days.
If you vomited within 3-4 hours of taking the pill, you should take a new pill no longer than 24 hours before your usual pill time. As long as you are not sick again, you should still be protected against pregnancy. If you are sick again or you do not take a new pill, your contraception will not be effective. If that is the case, retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
You should still be protected against pregnancy. Take your next pill as per your usual schedule.
You should still be protected against pregnancy if you experienced a few episodes of diarrhoea in a day/for less than 24 hours. Take your next pill as per your usual schedule. Speak to your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
If you have had severe diarrhoea for more than 24 hours, the pill may not have been fully absorbed and therefore may not be as effective. You should treat every 24 hours of severe diarrhoea as a missed pill. Retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
If you have had severe diarrhoea for more than 24 hours, the pill may not have been fully absorbed and therefore may not be as effective. You should treat every 24 hours of severe diarrhoea as a missed pill. Retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
You may be at risk of pregnancy. Please see your own doctor for advice and follow-up.
The protection against pregnancy will not be reduced if it has been less 12 hours. But, you should still take the following advice to ensure protection:
1) Take the tablet as soon as you remember.
2) Then take the next tablets at the usual time.
You may be at risk of pregnancy. Please see your own doctor for advice and follow-up.
The protection against pregnancy will be reduced. You should follow the below advice:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal (at your normal time). You may need to take two pills in one day.
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 9 days.
The protection against pregnancy may be reduced. For multiphasic pills, the advice on missed pills will depend on where in the cycle you are, and on which pill brand you are taking. Follow the advice below:
1) Always familiarise yourself with the instructions in the patient information leaflet (PIL) that comes with your pill packs.
2) Take note of when in your cycle you missed your pill - the advice will differ based on this.
- 2.1 At the beginning of your cycle you should take the missed pill and continue taking the pill as per the normal schedule. You should use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex the following 9 days to ensure protection against pregnancy.
- 2.2 If the missed pill was towards the end of your cycle you may be advised to skip the pill and start a new cycle (take the 1st pill of a new pill pack).
If you forget to take an inactive/placebo pill (the last pills in the pill pack), you do not need to take them later, as they do not contain active substances. But you should throw away the white tablet(s) you forgot to take, so that you do not prolong the period of inactive tablets. Prolongation may increase the risk of pregnancy. Continue to take the next tablet at the usual time. This is only relevant if you are taking a multiphasic pill with 28 pills (not 21).
If you vomited within 3 hours of taking the pill, you should take a new pill no longer than 24 hours after your normal pill time. If you are sick again or you do not take a new pill, your contraception will not be effective. If that is the case, retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
You should still be protected against pregnancy. Take your next pill as per your usual schedule.
If you have had severe diarrhoea for more than 24 hours, the pill may not have been fully absorbed and therefore may not be as effective. You should treat every 24 hours of severe diarrhoea as a missed pill. Retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
If you are less than 12 hours late, take the missed tablet as soon as possible, even if this means taking 2 tablets on the same day. This will ensure that contraceptive protection is maintained.
If you have missed a pill in the first week of your cycle, you should:
1) Take the last missed tablet as soon as possible and then continue to take the rest of the tablets in the normal manner.
2) Use extra contraceptive protection, such as a condom, or refrain from sex, for the next 7 days.
3) If you had sex in that 1st week (without additional contraception), you could become pregnant. Contact your doctor for advice as soon as possible. They may recommend you use emergency contraception. You should still continue taking your pill as normal.
If you are late by more than 12 hours, take the last missed tablet as soon as possible and then continue to take the rest of the tablets in the normal manner. In addition, use extra contraceptive protection, such as a condom for the next 7 days.
If you have fewer than seven tablets in your blister strip after you have missed taking a dose, you should:
1) Complete the blister strip and start the next blister strip without a break.
This will give you protection from when you took the last missed tablet. You may not have a period until the end of two blister strips, but this will not harm you. You may also have some bleeding on days when you take the tablets.
If you vomited within 3 hours of taking the pill, you should take a new pill no longer than 24 hours after your normal pill time. If you are sick again or you do not take a new pill, your contraception will not be effective. If that is the case, retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
You should still be protected against pregnancies. Take your next pill as per your usual schedule.
If you have missed more than one pill, you should:
1) Take the most recently missed pill and skip any previously missed pills.
2) Take your next pills as normal (this could mean taking two pills in one day)
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 7 days.
4) If you had sex in that 1st week (without additional contraception), you could become pregnant. Contact your doctor for advice as soon as possible. They may recommend you use emergency contraception. You should still continue taking your pill as normal.
If you have missed more than one pill, you should:
1) Take the most recent missed pill (skip any previously missed pills)
2) Take your next pills as normal (this could mean taking two pills in one day)
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 7 days.
If you missed a pill and have less than 7 pills left of your pack, you should:
1) Take the most recent missed pill (skip any previously missed pills)
2) Take your next pills as normal (this could mean taking two pills in one day)
3) When you finish the strip of pills, start the next strip the next day without a break.
4) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 7 days.
5) If you do not have a withdrawal bleed after you have finished the second strip, do a pregnancy test before starting another strip.
The desogestrel pill may not be as effective. The more pills you forget to take, the less effective your contraception is. You should follow the below advice:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal (at your normal time). You may need to take two pills in one day.
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 2 days.
You are still fully protected, as long as you:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can (as long as it is taken within 12 hours of your normal time).
2) Continue the pack as normal.
The desogestrel pill may not be as effective. The more pills you forget to take, the less effective your contraception is. You should follow the below advice:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal (at your normal time). You may need to take two pills in one day.
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 2 days.
You may be at risk of pregnancy. Please see your own doctor for advice and consider using an emergency contraceptive. Please note you should continue taking the pill as normal if you have used emergency contraception.
The desogestrel pill may not be as effective. The more pills you forget to take, the less effective your contraception is. You should follow the below advice:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal (at your normal time). You may need to take two pills in one day.
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 2 days.
If you vomited within 3 hours of taking the pill, you should take a new pill no longer than 12 hours after your normal pill time. If you are sick again or you do not take a new pill, your contraception will not be effective. If that is the case, retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
You should still be protected against pregnancy. Take your next pill as per your usual schedule.
You should still be protected against pregnancy. Take your next pill as per your usual schedule.
If you have had severe diarrhoea for more than 24 hours, the mini pill may not have been fully absorbed and therefore may not be as effective. You should treat every 24 hours of severe diarrhoea as a missed pill. Retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
Your contraception may not be as effective. You should follow the below advice:
1) Take the last missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal (at your normal time). You may need to take two pills in one day.
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 2 days.
You will not be protected against pregnancy if you have missed more than 2 pills. Unless a pregnancy can be ruled out, you should stop taking it until it can be confirmed (e.g. from a pregnancy test). If pregnancy can be ruled out, follow the advice below:
1) Continue taking the pill where you left off (or start a new pill pack).
2) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 2 days.
3) After seven days of taking the pill at a regular time, you will be protected again.
You are still fully protected, as long as you:
1) Take the pill as soon as you can (no later than 3 hours from your normal time)
2) Continue the pack as normal.
Your contraception may not be as effective. The more pills you forget to take, the less effective your contraception is. You should follow the below advice:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal (at your normal time). You may need to take two pills in one day.
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 2 days.
You may be at risk of pregnancy. Please see your own doctor for advice and consider using an emergency contraceptive. Please note you should continue taking the pill as normal if you have used emergency contraception.
Your contraception may not be as effective. The more pills you forget to take, the less effective your contraception is. You should follow the below advice:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal (at your normal time). You may need to take two pills in one day.
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 2 days.
If you vomited within 2 hours of taking the pill, you should take a new pill no longer than 3 hours after your normal pill time. If you are sick again or you do not take a new pill, your contraception will not be effective. If that is the case, retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
You should still be protected against pregnancy. Take your next pill as per your usual schedule.
You should still be protected against pregnancy. Take your next pill as per your usual schedule.
If you have had severe diarrhoea for more than 24 hours, the mini pill may not have been fully absorbed and therefore may not be as effective. You should treat every 24 hours of severe diarrhoea as a missed pill. Retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
Your contraception may not be as effective. You should follow the below advice:
1) The more pills you have missed, the more the effect against pregnancy is reduced.
2) Take the last missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
3) Continue the rest of the pack as normal (at your normal time). You may need to take two pills in one day.
4) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 7 days.
5) If this happened in the 1st week of the cycle (one or more of the first 7 pills), and you had sex the week before, you may be pregnant. Speak to your doctor for advice.
You are still fully protected, as long as you:
1) Take the pill as soon as you can (no later than 24 hours from your normal time).
2) Continue the pack as normal.
Your contraception may not be as effective. The more pills you forget to take, the more the effecicacy reduced. You should follow the below advice:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal (at your normal time). You may need to take two pills in one day.
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 7 days.
You should still be protected against pregnancy as long as you:
1) Take the missed pill and take the rest of the active pills as per normal schedule (24 pills).
2) Skip the 4 inactive (placebo) pills and start the new pill pack straight away.
You will now have a different start day of your cycle.
If you missed one of the last 4 pills of the pill pack it should have no impact (as these are hormone-free pills). You should:
1) Dispose of the missed pill and take the next scheduled pill at the correct time.
2) Be aware that only a specific type of mini pill brands contain inactive pills, and these should be clearly indicated and have a different colour to the rest of the pills (containing hormones). The instructions will be different if you have missed an active pill.
You may be at risk of pregnancy. Please see your own doctor for advice and follow-up. They may suggest you use a form of emergency contraception. You can continue taking your pills as normal if you have used an emergency contraception. You should also use a barrier method (such as a condom) if you have sex over the next 7 days.
Your contraception may not be as effective. The more pills you forget to take, the more the effecicacy reduced. You should follow the below advice:
1) Take the missed pill or start the new pill pack as soon as you can.
2) Continue the rest of the pack as normal (at your normal time). You may need to take two pills in one day.
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following 7 days.
If you vomited within 3-4 hours of taking the pill, you should take a new pill no longer than 24 hours after your normal pill time. If you are sick again or you do not take a new pill, your contraception will not be effective. If that is the case, retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
You should still be protected against pregnancy. Take your next pill as per your usual schedule.
If you experienced severe diarrhoea within 3 hours of taking the pill, you should take a new pill as soon as you can, and after no longer than 24 hours than your normal pill time. As long as you are feeling better and do not continue having diarrhoea, you should still be protected against pregnancy.
If you had severe diarrhoea within 3-4 hours of taking your pill and you have not taken a new one (within 24 hours of the normal pill time), or continue to have diarrhoea, you may not be protected. Retake this quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
You should still be protected against pregnancy. Take your next pill as per your usual schedule.
If you have had severe diarrhoea for more than 24 hours, the pill may not have been fully absorbed and therefore may not be as effective. You should treat every 24 hours of severe diarrhoea as a missed pill. Retake the quiz and follow the advice for a missed pill.
On rare occasions, the contraceptive vaginal ring can break. Vaginal damage has been reported in connection with the ring breaking. If you discover that your ring has broken, follow the below advice:
1) Dispose of that ring and insert a new ring as soon as possible.
2) Use additional contraception (eg a male condom) for the next 7 days.
3) Contact your doctor if you had intercourse before you discovered that the ring was broken.
If you are being sick (vomiting) or have diarrhoea, the contraceptive ring is still effective (unlike when you are taking the pill).
If you are being sick (vomiting) or have diarrhoea, the contraceptive ring is still effective (unlike when you are taking the pill).
If your ring-free break was no longer than 7 days, you are still protected from pregnancy. You should follow the below advice:
1) Put the new ring in as soon as possible (at your normal insertion time)
2) Replace the ring as per your normal schedule (1 ring should be replaced every seven days, at the same time)
If the ring-free break was longer than 7 days, you may not be protected against pregnancy. The longer the ring-free break lasts, the higher the risk of becoming pregnant. Follow the below advice:
1) Insert a new ring as soon as you remember.
2) Use additional contraception (such as a male condom) if you have intercourse in the next 7 days.
3) If you had intercourse during the ring-free break, there is a possibility that you could be pregnant. Talk to your doctor immediately and consider using a form of emergency contraception.
If the ring has been out of the vagina for less than 3 hours, it will still protect you from pregnancy. You should follow the below advice:
1) Wash the ring in cold or lukewarm water (do not use hot water).
2) Put the ring back in as soon as possible.
3) Replace the ring as per your normal schedule (1 ring should be replaced every seven days, at the same time).
You may not be protected against pregnancy. Take a pregnancy test and consult a doctor before inserting a new ring.
If the ring has been out of the vagina for more than 3 hours, you may not be protected against pregnancy. You should:
1) Wash the ring in cold or lukewarm water (do not use hot water)
2) Reinsert the ring into the vagina as soon as you remember, and leave the ring in place without interruption for at least 7 days.
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following seven days.
4) If you are in your 1st week and you had intercourse in the previous 7 days, there is a possibility that you could be pregnant. In this case, you must contact your doctor.
You may not be protected against pregnancy. You should dispose of that ring and choose one of the following two possibilities:
1) Insert a new ring immediately.
2) This will start the next 3-week period with the ring.
3) You may not have a period, but breakthrough bleeding and spotting may occur.
OR
1) Do not insert a new ring.
2) Have a period first and insert a new ring no later than 7 days from the time the previous ring was removed or fell out.
3) You should only choose this option if you have used NuvaRing continuously for the last 7 days.
If you are being sick (vomiting) or have diarrhoea, the contraceptive patch is still effective (unlike when you are taking the pill).
If you are being sick (vomiting) or have diarrhoea, the contraceptive patch is still effective (unlike when you are taking the pill).
Follow the below advice to ensure you are still protected:
1) Try to attach it again or put on a new transdermal patch immediately (so it has been off for less than 24 hours).
2) Use a new patch if the other one is no longer sticky, has stuck together or to something or if it's fallen off before (do not attempt to use tape or wraps to stick the old one back on).
3) Your "patch change day" must remain unchanged.
The patch may not be as effective. The longer you have been without the patch, the less effective your contraception will be. You should follow the advice below:
1) Immediately start a new 4-week cycle by applying a new transdermal patch.
2) You now have a new day 1 and a new "patch change day".
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following seven days (the 1st week of the new cycle).
The patch may not be as effective. The longer you have been without the patch, the less effective your contraception will be. You should follow the advice below:
1) Immediately start a new 4-week cycle by applying a new transdermal patch.
2) You now have a new day 1 and a new "patch change day".
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following seven days (the 1st week of the new cycle).
Follow the below advice to ensure you are still protected:
1) Try to attach it again or put on a new transdermal patch immediately (so it has been off for less than 24 hours).
2) Use a new patch if the other one is no longer sticky, has stuck together or to something or if it's fallen off before (do not attempt to use tape or wraps to stick the old one back on).
3) Your "patch change day" must remain unchanged.
The patch may not be as effective. The longer you have been without the patch, the less effective your contraception will be. You should follow the advice below:
1) Immediately start a new 4-week cycle by applying a new transdermal patch.
2) You now have a new day 1 and a new "patch change day".
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following seven days (the 1st week of the new cycle).
The patch may not be as effective. The longer you have been without the patch, the less effective your contraception will be. You should follow the advice below:
1) Immediately start a new 4-week cycle by applying a new transdermal patch.
2) You now have a new day 1 and a new "patch change day".
3) Use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following seven days (the 1st week of the new cycle).
If you forget to put on the transdermal patch in your cycle's 1st week, you may have a particularly high risk of becoming pregnant. Follow the advice below:
1) You must use additional non-hormonal contraception for one week (seven days).
2) Put on the first patch of the new cycle as soon as you remember.
3) You now have a new day 1 and a new "patch change day".
If you are on the 4th week of the cycle, you should still be protected against pregnancies. If you left the patch on for too long (forgot to remove it), take it off as soon as you remember. Follow the below advice to stay protected:
1) Start the next cycle on the usual "patch change day", the day after day 28.
2) Continue replacing them weekly, on the same day at the same time.
3) There is no need for additional contraception.
You should still be protected, provided you follow the below advice:
1) Attach a new patch as soon as you remember (within 48 hours).
2) Replace the following patch on the usual "patch change day".
3) No additional contraception is necessary.
If you forget to change the patch for more than 2 days, you can become pregnant. The longer you have been without the patch, the lower the effectiveness will be. You should follow the advice below:
1) Immediately start a new 4-week cycle by applying a new patch.
2) You now have a new day 1 and a new "patch change day".
3) You must use a barrier contraceptive method if you have sex, for the following seven days (1st week of cycle).
Missing one or more pills
Taking a tablet more than 24 hours late (or 12 hours for some COCPs) counts as a missed pill. If you miss one tablet, the general advice is to take the missed tablet as soon as possible, even if this means taking 2 tablets in 1 day. It is also advisable to use barrier contraception for at least 7 days. If you have had unprotected sex during that period, you may need to use emergency contraception.
Vomiting and diarrhoea
If you have severe diarrhoea or you vomit within 3 hours of taking the pill, it may not be absorbed properly and therefore might not be as effective. If this happens, you should follow the advice for a missed pill where appropriate.
What are the side effects of ‘the pill’?
The combined pill can cause side effects, especially within the first few months of taking it.
Some side effects of the combined contraceptive pill are:
- headaches
- breast tenderness
- spotting between periods or breakthrough bleeding
- mood swings
- changes in your sex drive
- weight gain
See our diagram below for more side effects.
 Neurological
Neurological
Headaches are a common side effect of contraceptive pills. More serious headaches and migraines are less common.
GastricStomach upsets are fairly common and can occasionally result in vomiting. Some women experience slight weight gain, but weight loss is rare.
GynaecologicalSome women who take a contraceptive pill will experience changes in their sex drive.
BreastIt is quite common to experience breast soreness or tenderness in the first few weeks or months after starting a new pill. In very rare cases, you may notice breast discharge.
Click on the relevant area of the body to find out about how it may be affected by your contraceptive pill
Most of the common side effects are mild. However, if you experience any worrying side effects, talk to your doctor. They may suggest you try a different contraceptive.
What are the risks of taking ‘the pill’?
While hormonal contraception is safe for most women, some health factors may increase your risk of side effects and complications.
This medication may not be suitable if you:
- are over the age of 35 and smoke
- have a high BMI
- have conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes (with complications), or liver or gallbladder disease
- have frequent migraines
- have a personal or family history of blood clots
- have breast cancer
- have heart conditions such as a stroke
The pill may also affect other medicines, such as:
- medicines for epilepsy
- medicines for HIV
- certain antibiotics
- St John’s Wort (a herbal remedy)
- certain antifungals
These medicines may reduce the effectiveness of the pill. In many cases, women who can't use this treatment may be able to use another form of hormonal contraception, such as the POP.
Cancer
Taking the combined pill reduces your risk of ovarian, colorectal and endometrial cancer. Research has shown that it slightly increases the risk of breast cancer and cervical cancer compared to people who do not take it. However, this risk reduces and eventually reverses after 10 years of stopping it.
Make sure you monitor your breasts or any other health changes.
Blood clots
Another complication is a small increase in the risk of blood clots (thrombosis). While the risk is low, your doctor will check if you have certain risk factors before prescribing this medication.
If you have any signs of a blood clot such as swelling, redness or warmth in the leg, seek immediate medical attention.
What are the side effects of coming off the pill?
Although the contraceptive pill is safe and effective, some people may decide that it is not for them, or want to take a break from taking it. It’s important to understand what effects this might have on your body.
Some side effects of stopping the pill might include:
- headaches
- weight change
- acne
- mood swings
- missed periods or irregular periods
Can I buy the pill online?
If you are using a combined contraceptive pill, you can order it online at euroClinix. All you have to do is complete a quick online medical questionnaire. Then, one of our doctors will review your responses to ensure it's right for you. Once approved, your order will be dispensed and dispatched with fast, free delivery.
- What is the combined oral contraceptive pill?
- How does the pill work?
- What types of combined oral contraceptive pills are available?
- What are the benefits of taking birth control pills?
- How do I take it?
- What do I do if I miss a pill?
- What are the side effects of ‘the pill’?
- What are the risks of taking ‘the pill’?
- What are the side effects of coming off the pill?
- Can I buy the pill online?
Further reading

Can you use hormonal contraception after 40?
Reviewed by Dr. Caroline Fontana
Understanding and managing side effects of the pill
Reviewed by Dr. Caroline FontanaSelect
medicationFill out a short
medical formDoctor issues
prescriptionMedication sent
from pharmacy